Maintaining good gut health is essential for overall well-being, as it influences not only digestion but also immune function and mental health. Recent studies highlight the significant role of gut microbiota in our bodies, emphasizing the importance of a balanced diet rich in fiber, prebiotics, and probiotics. Incorporating foods that promote gut health, such as fermented products, can vastly improve your digestive system. As we delve into this topic, you’ll discover effective tips and dietary choices that foster a thriving gut microbiome, ultimately enhancing your quality of life.
Understanding Gut Health
Gut health refers to the overall function and balance of microorganisms in the gastrointestinal tract. The gut houses trillions of bacteria, viruses, and other microbes that play a crucial role in digestion, nutrient absorption, and immune function. Maintaining a well-balanced gut microbiome is essential for promoting gut health and overall well-being.
Here are several key aspects to understand about gut health:
- Diversity of Microbiota: A diverse gut microbiome enhances gut health by providing various beneficial bacteria, which can help stave off harmful pathogens.
- Gut Barrier Function: The gut lining acts as a barrier, preventing harmful substances from entering the bloodstream. A healthy gut ensures that this barrier remains intact.
- Digestive Processes: Proper gut health is vital for effective digestion, as it affects how well the body breaks down food and absorbs nutrients.
- Immune System Interaction: Approximately 70% of the immune system resides in the gut. Therefore, a healthy gut directly supports a robust immune response.
In summary, understanding gut health involves appreciating the complex interactions within the gut microbiome and their effects on overall health. By focusing on maintaining a diverse and balanced gut flora, you can optimize your gut health and enhance your quality of life.
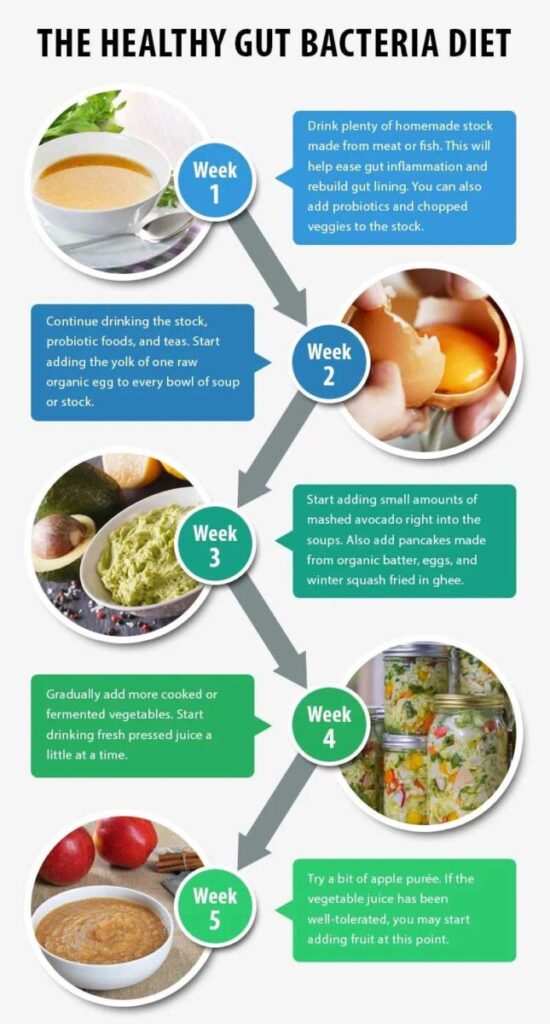
The Importance of Gut Microbiota
Gut microbiota, the community of microorganisms residing in our digestive tract, plays a crucial role in maintaining overall gut health. These microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi, greatly influence various bodily functions. Here’s why gut microbiota is so important:
- Digestive Efficiency: A balanced microbiota helps break down complex carbohydrates and synthesize essential nutrients, improving digestion and nutrient absorption.
- Immune System Support: Approximately 70% of our immune system resides in the gut. A healthy microbiota contributes to a robust immune response, defending against pathogens and reducing the risk of infections.
- Metabolism Regulation: Different gut bacteria can influence how our bodies metabolize food. For example, some bacteria may promote fat storage while others help in burning fat.
- Mental Health Link: Recent studies suggest a connection between gut microbiota and mental well-being. A healthy gut can positively affect mood and cognitive functions through the gut-brain axis.
To maintain a balanced microbiota, consider incorporating the following in your diet:
| Food Type | Impact on Gut Microbiota |
|---|---|
| Fermented Foods | Introduces beneficial bacteria |
| Prebiotic Fiber | Nourishes existing good bacteria |
| Processed Foods | May disrupt microbiota balance |
In essence, maintaining a diverse and balanced gut microbiota is essential for optimal gut health, influencing not just digestion but overall well-being.
Foods That Promote Gut Health
To support gut health, incorporating specific foods into your diet can make a significant difference. These foods work in harmony with your digestive system, enhancing the diversity and balance of gut microbiota. Here are some key food groups to consider:
- Fruits and Vegetables: Rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, they provide essential nutrients that nourish beneficial gut bacteria. Examples include:
- Bananas
- Apples
- Spinach
- Broccoli
- Whole Grains: Whole grains are excellent sources of fiber, which promotes regular bowel movements and supports a healthy gut lining. Popular options include:
- Brown rice
- Quinoa
- Oats
- Nuts and Seeds: These are packed with healthy fats and fiber, supporting the growth of good bacteria. Choose:
- Almonds
- Chia seeds
- Flaxseeds
- Lean Proteins: Including lean proteins, such as poultry and fish, provides amino acids that aid in maintaining the gut’s structural integrity.
- Fermented Foods: Foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi contain probiotics, which are live bacteria that promote gut health and improve digestion.
Incorporating a variety of these foods into your daily meals can enhance your overall gut health, contribute to better digestion, and support your immune system. Prioritize these food choices for a healthier digestive tract!
Prebiotics and Probiotics Explained
Understanding the roles of prebiotics and probiotics is essential for promoting gut health. Both components work synergistically to maintain and enhance a balanced gut microbiota, crucial for overall well-being.
Prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that feed beneficial gut bacteria. They stimulate the growth and activity of these microorganisms, thereby improving gut health. Key sources of prebiotics include:
- Garlic
- Onions
- Asparagus
- Bananas
- Whole grains
By incorporating these foods into your diet, you provide the fuel necessary for your gut’s friendly bacteria to thrive.
Probiotics, on the other hand, consist of live beneficial bacteria that contribute directly to gut health. These microorganisms help in restoring balance to the gut microbiome, especially after disturbances such as antibiotic use. Common sources of probiotics include:
- Yogurt
- Kefir
- Sauerkraut
- Kimchi
- Miso
Comparison of Prebiotics and Probiotics
| Feature | Prebiotics | Probiotics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Indigestible food fibers | Live beneficial bacteria |
| Function | Nourish beneficial bacteria | Introduce good bacteria |
| Sources | Whole grains, fruits, vegetables | Fermented foods, supplements |
| Impact on Gut | Stimulates growth of good bacteria | Restores balance of gut flora |
Incorporating both prebiotics and probiotics into your diet is a pivotal step in enhancing your gut health, leading to improved digestion and overall wellness.

The Role of Fiber in Digestive Health
Fiber plays a crucial role in maintaining gut health by fostering effective digestion and promoting a balanced gut microbiota. It is classified into two primary types: soluble and insoluble fiber, both of which contribute distinctly to digestive health.
Soluble Fiber:
- Dissolves in water to form a gel-like substance.
- Slows digestion, which helps regulate blood sugar levels.
- Fermented by gut bacteria, producing short-chain fatty acids that nourish colon cells.
Insoluble Fiber:
- Does not dissolve in water.
- Adds bulk to stool, promoting regular bowel movements.
- Helps prevent constipation by speeding up the passage of food through the digestive tract.
Benefits of Fiber for Gut Health:
- Promotes Regularity: A high-fiber diet can reduce the risk of constipation.
- Feeds Good Bacteria: Soluble fiber serves as food for beneficial gut bacteria, enhancing gut microbiota diversity.
- Reduces Gut Inflammation: Fiber can lower inflammatory markers, supporting overall gut health.
Recommended Daily Intake:
- Women: 25 grams
- Men: 38 grams
Incorporating fiber-rich foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, can significantly enhance your gut health. Aim for a mix of both soluble and insoluble fiber to fully reap the digestive benefits. By prioritizing fiber in your diet, you can support not just your gut but your overall well-being.
Please click here to buy books about Nutrition for Gut Health from Amazon by clicking here.
Fermented Foods for a Healthy Gut
Incorporating fermented foods into your diet can significantly boost gut health. These foods undergo a natural fermentation process, enriching them with probiotics—beneficial bacteria that enhance gut microbiota.
Benefits of Fermented Foods for Gut Health:
- Enhanced Digestion: Fermented foods help break down nutrients, improving their absorption and alleviating bloating.
- Stronger Immune System: Probiotics in these foods support the immune system by maintaining a balanced gut microbiome.
- Mood Regulation: Research suggests that a healthy gut can influence mental well-being through the gut-brain connection.
Popular Fermented Foods to Add to Your Diet:
| Fermented Food | Probiotic Content | Additional Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Yogurt | High | Calcium-rich, aids in lactose digestion |
| Sauerkraut | Moderate | High in Vitamin C and fiber |
| Kimchi | High | Packed with antioxidants |
| Kefir | Very High | Contains a diverse range of probiotics |
| Miso | Moderate | Source of protein and antioxidants |
Incorporating Fermented Foods:
- Start with small servings, gradually increasing your intake to avoid digestive discomfort.
- Combine fermented foods with other dishes, such as adding yogurt to smoothies or sauerkraut to salads.
By regularly including fermented foods in your diet, you can promote a thriving gut microbiome, leading to improved gut health and overall wellness.
Diets to Avoid for Optimal Gut Health
Maintaining optimal gut health is essential for overall wellness. However, certain diets can disrupt the delicate balance of gut microbiota, leading to various health issues. Here are some diets to avoid for improved gut health:
- High-Sugar Diet: Excessive sugar promotes harmful bacteria growth while inhibiting beneficial ones. This imbalance can lead to inflammation and other gut issues.
- Processed Foods: Packed with preservatives, artificial additives, and unhealthy fats, processed foods can negatively affect gut health by decreasing microbial diversity.
- Low-Fiber Diet: Fiber acts as a prebiotic, feeding healthy gut bacteria. Diets lacking fiber can harm gut health and hinder digestive processes.
- High-Fat Diet: Diets rich in saturated and trans fats may contribute to digestive disorders. These fats can promote inflammation and disrupt the gut barrier function.
- Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Chronic alcohol intake can lead to harmful gut bacteria flourishing while damaging the gut lining, leading to leaky gut syndrome.
In summary, prioritizing whole foods, rich in fiber and low in sugar and processed ingredients, supports gut health. Maintaining a well-rounded diet is critical for nurturing beneficial bacteria, preventing digestive issues, and enhancing overall well-being. Thus, avoiding these detrimental eating patterns can significantly contribute to optimal gut health.

Hydration and Gut Function
Maintaining proper hydration is vital for promoting gut health. Water serves as a key component in several digestive processes, influencing how efficiently our bodies absorb nutrients and eliminate waste. Here’s how hydration affects gut function:
- Fluid Balance: Sufficient water intake helps maintain fluid balance, ensuring that digestive juices are adequately produced. This aids in the breakdown of food and absorption of nutrients.
- Constipation Prevention: Staying hydrated can significantly reduce the risk of constipation. Water softens stool, making it easier to pass through the intestines. A hydrated gut works more efficiently, enhancing overall gut health.
- Microbiota Support: Optimal hydration helps support the growth of beneficial gut bacteria. A well-hydrated environment fosters a diverse microbiota, which is essential for healthy digestion and immune function.
To assess your hydration status, consider the following:
| Indicator | Hydrated | Dehydrated |
|---|---|---|
| Urine Color | Light yellow | Dark yellow |
| Energy Levels | Stable | Low |
| Digestive Comfort | Good | Bloating |
Incorporating water-rich foods, such as fruits and vegetables, can further enhance hydration. Remember, keeping yourself well-hydrated not only benefits digestion but also plays an important role in maintaining overall gut health. So, drink plenty of water throughout the day to keep your gut functioning optimally!
The Connection Between Gut Health and Mental Well-being
Emerging research highlights a fascinating link between gut health and mental well-being. This connection is partly due to the gut-brain axis, a complex communication network between the gastrointestinal tract and the brain. Understanding this relationship is crucial for enhancing both mental and physical health.
Key factors in the gut-brain connection include:
- Microbiota Influence: Gut bacteria release neurotransmitters, such as serotonin, which significantly impacts mood and emotional stability.
- Inflammation: An unhealthy gut can lead to inflammation, which is linked to mood disorders like anxiety and depression.
- Nutrition: Diets rich in fiber and fermented foods can improve gut health, allowing for better mental clarity and emotional health.
Here’s a comparison of the effects of a nutritious diet versus a poor diet on mental well-being:
| Aspect | Nutritious Diet (Promoting Gut Health) | Poor Diet (Harming Gut Health) |
|---|---|---|
| Gut Microbiota | Promotes diversity and balance | Causes imbalance and dysbiosis |
| Neurotransmitter Levels | Increases serotonin and dopamine | Lowers effective neurotransmitter production |
| Mental Health | Enhances mood and reduces anxiety | Intensity of stress and anxiety increases |
In conclusion, maintaining optimal gut health plays a vital role in supporting mental well-being. Prioritizing a balanced diet rich in nutrients can profoundly improve both gut function and your overall emotional state.
Tips for Maintaining Gut Health
Maintaining optimal gut health is essential not only for digestion but also for overall well-being. Here are some actionable tips to help you nurture your gut:
- Eat a Diverse Range of Foods: Incorporate various fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins into your diet. A diverse diet supports a varied gut microbiota, which is crucial for gut health.
- Include Probiotics: Foods rich in probiotics, such as yogurt, kefir, and fermented vegetables, can introduce beneficial bacteria to your gut. Aim to consume these regularly for improved gut health.
- Prioritize Fiber Intake: High-fiber foods such as beans, whole grains, and oats not only support digestion but also promote the growth of healthy gut bacteria. Aim for at least 25 grams of fiber daily.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking enough water is vital for digestion and nutrient absorption. Proper hydration supports a healthy gut environment.
- Limit Processed Foods: Highly processed foods can negatively impact gut health by promoting the growth of harmful bacteria. Focus instead on whole, natural foods.
- Manage Stress Levels: Stress can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria. Engage in mindfulness practices, such as yoga or meditation, to promote gut health.
- Get Regular Exercise: Physical activity enhances gut motility and can foster a healthy microbiome. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise weekly.
By integrating these simple yet effective tips into your daily routine, you can enhance your gut health, thus improving your overall health and wellness.

When to Seek Professional Help
Maintaining gut health is essential for overall well-being, but sometimes self-care is not enough. Recognizing when to seek professional help can be crucial for addressing persistent issues. Here are key indicators that it might be time to visit a healthcare provider:
- Persistent Digestive Issues: If you experience ongoing symptoms such as:
- Chronic bloating
- Frequent gas
- Severe diarrhea or constipation
- Acid reflux or heartburn
- Significant Weight Changes: Unexplained weight gain or loss can signal underlying gut health issues that require attention.
- Food Intolerances or Allergies: Developing new sensitivities to foods can affect your gut balance. It may be time to consult an expert to understand the cause and achieve better gut health.
- Fatigue and Mood Changes: Since gut health influences mental well-being, persistent fatigue, anxiety, or depression can indicate a disrupted gut microbiome.
- Skin Problems: Conditions like eczema or persistent acne can sometimes be linked to gut health.
If you notice any of these signs, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional who can provide a tailored approach to improving your gut health. Remember, everyone’s digestive system is different, and personalized guidance can lead to better outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is gut health and why is it important?
Gut health refers to the balance of microorganisms living in the digestive tract, particularly in the intestines. This balance is crucial because it influences not only digestion and nutrient absorption but also the overall immune system, mental health, and even the risk of certain chronic diseases. A healthy gut environment can contribute to greater energy levels, improved mood, and a reduced risk for conditions like obesity, diabetes, and autoimmune diseases.
What foods are best for promoting gut health?
Foods rich in fiber such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes can significantly promote gut health. Fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi are also beneficial as they contain probiotics, the beneficial bacteria that help maintain the gut flora balance. Additionally, foods that are high in polyphenols, found in berries, green tea, and olive oil, can support the growth of good gut bacteria, enhancing digestion and overall health.
How do probiotics and prebiotics differ in supporting gut health?
Probiotics are live beneficial bacteria that can be consumed through supplements or fermented foods, directly adding to the gut microbiome. Prebiotics, on the other hand, are types of fiber that feed these beneficial bacteria. Prebiotics help stimulate the growth and activity of healthy gut bacteria which, in turn, enhances gut health and overall digestion. Including both in your diet is essential for a well-rounded approach to supporting gut health.
Can my gut health affect my mental health?
Yes, there is a significant connection between gut health and mental health, often referred to as the gut-brain axis. A balanced gut microbiome can influence brain chemistry, impacting mood and cognitive functions. Research indicates that imbalances in gut bacteria may be linked to anxiety, depression, and other mental health issues. Therefore, maintaining a healthy diet that supports gut health can also aid in enhancing mental well-being.
How can I tell if my gut health is poor?
Indicators of poor gut health can vary, but common symptoms include digestive issues like bloating, gas, constipation, or diarrhea. Additionally, experiencing frequent food sensitivities, sudden weight changes, fatigue, and even skin irritations can be signs of an imbalanced gut microbiome. If you’re noticing these symptoms persistently, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for an appropriate assessment and guidance.
