Women experience health conditions in unique ways, shaped by a complex interplay of biological, hormonal, and social factors. Understanding these differences is crucial for improving health outcomes and ensuring equitable healthcare for all. As we dive into this important topic, we will explore how various elements, including socioeconomic impacts and social expectations, influence the health of women. By raising awareness and empowering women through education, we can pave the way for better understanding and management of health conditions that specifically affect them.
Understanding Gender Differences in Health
Gender differences play a crucial role in how individuals experience health conditions. Women and men often show distinct responses to diseases, treatments, and overall health management. Here’s why understanding these differences is essential:
- Biological Disparities: Women’s bodies have unique biological features that influence health conditions, such as reproductive systems and variations in metabolism. For instance, certain auto-immune disorders are more prevalent in women, underscoring the need for gender-specific research.
- Hormonal Influences: Fluctuations in hormones, particularly during menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause, can affect how women react to various health conditions. This variance may lead to different symptom presentations or intensity compared to men.
- Health Risk Profiles: Men and women face different risks for chronic diseases. For instance, while men may be more inclined toward cardiovascular diseases, women are more susceptible to conditions like osteoporosis and depression.
- Behavioral Factors: Societal norms may impact health behaviors. Women are often more proactive in seeking healthcare, which could lead to earlier diagnosis and treatment of health conditions.
By appreciating these gender-specific nuances, healthcare providers can better tailor interventions and improve outcomes for both women and men. Ultimately, fostering awareness of these differences enhances the conversation around health conditions, paving the way for a more equitable health landscape.
Biological Factors Influencing Health Conditions
Biological factors significantly contribute to how women experience health conditions differently than men. Understanding these differences is crucial for tailoring effective healthcare strategies. Here are several key biological factors:
- Genetics: Women often possess two X chromosomes, which provide a genetic advantage in combating certain diseases. This genetic diversity can influence their susceptibility to various health conditions compared to men.
- Immune System: Women generally have stronger immune responses. While this can lead to a lower incidence of infections, it might also increase the risk of autoimmune diseases, where the body mistakenly attacks its own tissues.
- Hormonal Cycles: The fluctuations of hormones such as estrogen and progesterone play a vital role in women’s health. These hormones can affect how women respond to medications, as well as their vulnerability to conditions like depression or anxiety.
- Body Composition: Women typically have a higher percentage of body fat compared to men, which can influence the prevalence and severity of certain health conditions, such as heart disease.
To summarize, biological factors interplay to shape the health conditions women face. Acknowledging these differences not only enhances our understanding but also drives awareness for gender-specific health initiatives. Therefore, continued research is essential to developing tailored health solutions that address the unique biological needs of women.
The Role of Hormones in Women’s Health
Hormones play a pivotal role in shaping women’s health conditions, influencing everything from mood to metabolism. Specifically, estrogen and progesterone are two primary hormones that undergo fluctuations throughout a woman’s life, particularly during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause.
Key Hormonal Influences:
- Menstrual Cycle: Hormonal changes directly affect a woman’s energy levels and mood, leading to premenstrual syndrome (PMS) for many. These symptoms can vary significantly among women, impacting their daily lives.
- Pregnancy: During pregnancy, hormone levels surge, which can lead to unique health conditions such as gestational diabetes or postpartum depression. Understanding these changes can promote better prenatal care.
- Menopause: The transition into menopause involves decreased hormone production, leading to symptoms like hot flashes and increased risk of osteoporosis. Awareness of these health conditions can prepare women for this natural phase.
Comparison of Hormonal Effects:
| Aspect | Before Menopause | After Menopause |
|---|---|---|
| Estrogen Levels | Higher | Significantly lower |
| Risk of Heart Disease | Lower | Increased |
| Mood Stability | More stable | More susceptible to mood swings |
Recognizing these hormonal influences is crucial not only for understanding health conditions, but also for guiding preventive measures and treatments tailored specifically to women’s needs. By prioritizing women’s health from a hormonal perspective, we empower women to seek appropriate care and achieve better health outcomes overall.
Socioeconomic Impacts on Health Disparities
Socioeconomic status significantly affects how women experience health conditions. Women from lower-income backgrounds frequently encounter barriers that influence their overall health and wellbeing. These barriers can include:
- Limited Access to Healthcare: Women in lower socioeconomic tiers often have less access to essential health services. This disparity can lead to late diagnosis of health conditions and inadequate treatment.
- Education and Health Literacy: Education plays a crucial role in understanding health information. Women with less education may struggle to recognize symptoms of health conditions or follow health recommendations.
- Employment and Financial Stability: Job insecurity can prevent women from seeking timely medical care. Financial stress can exacerbate existing health conditions, creating a vicious cycle.
- Social Support Systems: Women without robust social networks may lack emotional support crucial for navigating health issues. This lack of support can lead to a decline in mental and physical health.
Comparison of Health Outcomes by Socioeconomic Status
| Socioeconomic Status | Access to Healthcare | Health Literacy | Health Conditions Prevalence |
|---|---|---|---|
| High | High | High | Lower incidence |
| Medium | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate incidence |
| Low | Low | Low | Higher incidence |
In summary, socioeconomic factors dramatically shape how women experience health conditions. By addressing these disparities, we can improve health outcomes for women across all economic strata, fostering a healthier future.

How Social Expectations Shape Health Outcomes
Social expectations significantly influence how women experience and manage health conditions. These expectations often stem from cultural norms, stereotypes, and societal roles, which can manifest in various ways:
- Health-Seeking Behavior: Women may delay seeking medical help due to societal pressure to prioritize family and work over personal health. This can lead to undiagnosed or untreated health conditions.
- Stigmatization: Certain health conditions, particularly mental health issues, can carry stigma. Women often feel societal pressure to maintain a façade of strength, preventing them from discussing or addressing their health conditions openly.
- Caregiver Roles: Women frequently take on caregiving responsibilities for family members, which can detract from their own self-care. This multitasking can exacerbate existing health conditions or lead to new ones.
- Media Representation: The portrayal of women in media can influence self-perception and mental health. Unrealistic beauty standards or expectations regarding motherhood can lead to anxiety and stress, further complicating health outcomes.
- Access to Resources: Social expectations can dictate which health services women prioritize. For instance, women may focus more on reproductive health due to cultural norms, while neglecting other crucial health conditions.
By acknowledging these societal influences, we can work towards creating a more supportive environment that empowers women to address their health conditions proactively and effectively.
Awareness and Research on Women’s Health Issues
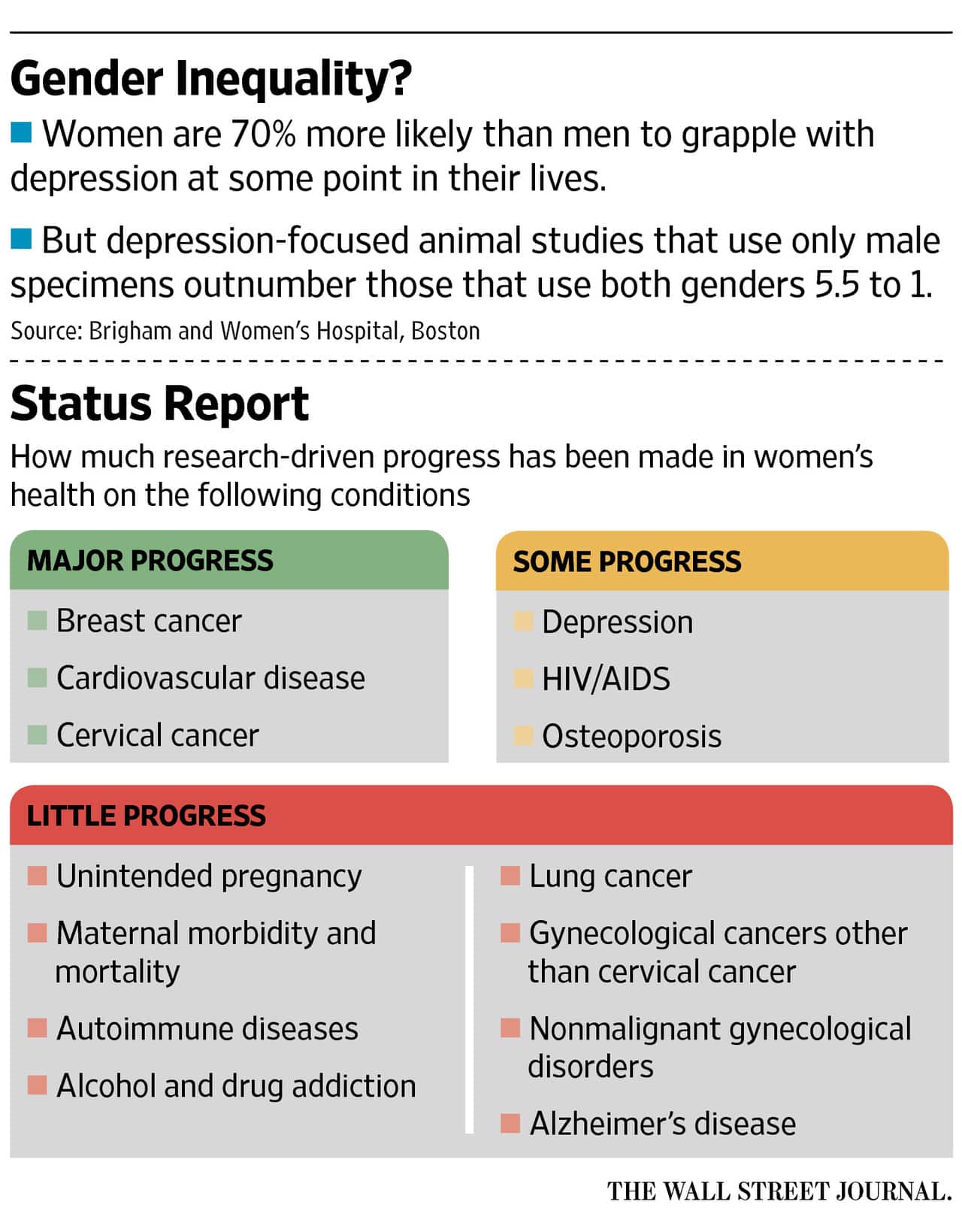
Awareness and research into women’s health issues play a crucial role in understanding how women experience various health conditions differently than men. Historically, many health studies predominantly focused on male populations, leading to significant gaps in data concerning women’s health. Fortunately, this trend is gradually changing as researchers recognize the importance of gender-specific studies.
Here are a few key points highlighting the discrepancies in awareness and research:
- Underrepresentation in Research: Women have often been underrepresented in clinical trials. This has limited our understanding of how certain health conditions, such as heart disease and autoimmune disorders, manifest uniquely in women.
- Funding Disparities: Research funding for women’s health issues remains disproportionately low compared to other health conditions. As a result, important areas like reproductive health and menopause require more targeted financial support.
- Impacts of Social Awareness: Increasing advocacy for women’s health has led to greater public attention and funding for research. Social media campaigns and community outreach programs are fostering a more informed population.
- Emerging Research Areas: New studies focus on issues such as pregnancy-related complications, mental health disorders, and gender-specific treatments. These efforts validate women’s unique experiences and ensure their health conditions receive the attention they deserve.
As awareness grows, the research landscape continuously evolves, paving the way for improved outcomes and healthcare strategies tailored to women’s health conditions. Empowering women through education and advocacy is essential for bridging these gaps and fostering a healthier future.
Access to Healthcare for Women
Access to healthcare plays a crucial role in addressing women’s unique health conditions. While significant strides have been made, challenges still persist that affect women’s ability to receive adequate care. Understanding these barriers helps in creating a more equitable health landscape.
Key Barriers to Access:
- Financial Constraints: Many women face economic hardships that limit their access to necessary healthcare services. This disparity often stems from lower wages and job instability.
- Geographical Location: Women in rural or underserved areas may lack nearby healthcare facilities or specialists, making it difficult for them to receive timely care.
- Cultural Stigmas: Cultural perceptions can influence women’s willingness to seek help for certain health conditions, particularly mental health issues.
- Lack of Insurance: A significant number of women remain uninsured, leading to delayed treatments or avoidance of preventive care.
The Importance of Equal Access:
Equal access to healthcare can drastically improve health outcomes for women. When women receive proper care, they experience:
- Improved management of chronic health conditions
- Enhanced mental health support
- Higher rates of preventive healthcare use
In conclusion, addressing the barriers to access can empower women to lead healthier lives, reduce the prevalence of neglected health conditions, and ultimately create a healthier society for everyone.

Women’s Responses to Treatments
Understanding how women respond to treatments is crucial in addressing the varied health conditions they face. Research shows that treatment efficacy can differ between genders due to several factors, including biological and hormonal differences. Here are some key points to consider:
- Hormonal Influence: Women’s hormonal fluctuations throughout their menstrual cycle can impact how they metabolize medications. For instance, certain drugs may have reduced effectiveness during specific phases of the cycle.
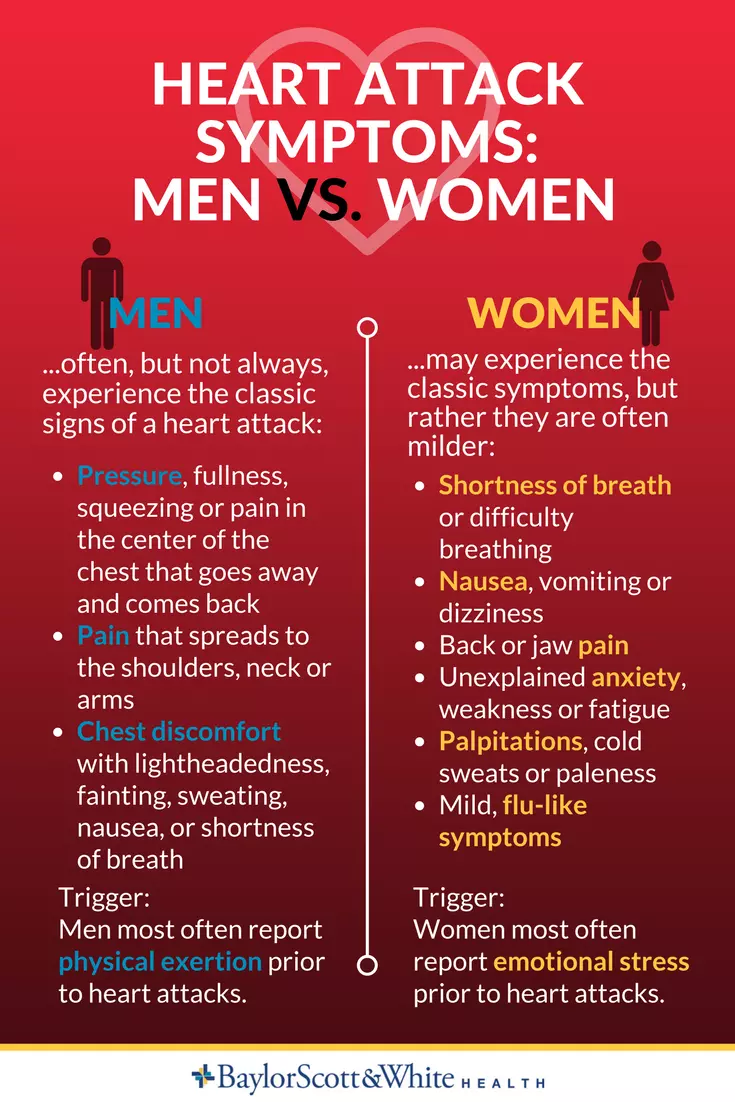
- Side Effects: Studies suggest that women often experience side effects more intensely than men. For example, while medications for pain relief may work similarly, women report higher rates of side effects such as nausea and fatigue.
- Adherence to Treatment: Women are generally more proactive in seeking healthcare, leading to higher adherence rates to prescribed treatments. They often prioritize their health, which positively affects outcomes.
- Chronic Conditions: Women often live longer with chronic health conditions, such as autoimmune diseases, and may respond differently to treatments than men. Tailoring therapies considering these differences enhances treatment effectiveness.
| Gender | Treatment Response | Side Effect Intensity |
|---|---|---|
| Women | Varied | Higher |
| Men | More uniform | Lower |
In summary, recognizing these variations in women’s responses to treatments is essential for tailored healthcare. By improving treatment approaches, we can empower women to manage their health conditions more effectively.
Mental Health: Gender-Specific Considerations
Exploring mental health brings fascinating insights, particularly when considering gender-specific considerations. Women and men often experience mental health conditions differently due to a combination of biological, social, and psychological factors.
Key factors influencing these differences include:
- Hormonal Variations: Fluctuating hormone levels can impact women’s moods and emotions, leading to conditions like depression and anxiety. These conditions may often show more severe symptoms in women.
- Social Expectations: Women often face unique societal pressures, which can contribute to higher stress levels. Balancing work, family, and social roles can lead to increased vulnerability to mental health issues.
- Coping Strategies: Research shows that women tend to internalize stress, which can escalate mental health conditions. In contrast, men may externalize through behaviors that could complicate their recovery.
| Consideration | Women | Men |
|---|---|---|
| Expression of Emotion | More open | Often reserved |
| Coping Mechanism | Internalization | Externalization |
| Common Conditions | Depression, Anxiety | Substance Abuse, Anger |
By understanding these gender-specific factors, we can better address women’s unique health conditions and encourage tailored support strategies. Empowering women to prioritize their mental health is essential—not just for their well-being, but also for fostering healthier communities.
Empowering Women through Health Education
Empowering women through health education stands as a pivotal strategy for addressing the unique health conditions they face. By providing women with comprehensive knowledge about their health, we can improve health outcomes and foster a proactive approach to personal well-being.
Benefits of Health Education for Women:
- Informed Decision-Making: Education equips women to make informed choices about their health, including prevention strategies and treatment options.
- Awareness of Health Conditions: Understanding specific health conditions that disproportionately affect women, such as autoimmune disorders or reproductive health issues, enables them to seek timely care.
- Self-Advocacy: With knowledge, women can advocate for themselves in healthcare settings, ensuring that their concerns are heard and addressed.
- Community Support: Health education often fosters networks where women can share experiences, thus creating a supportive community.
Comparison of Health Education Impact:
| Aspect | With Education | Without Education |
|---|---|---|
| Understanding of Health Conditions | High | Low |
| Proactive Healthcare Participation | Increased | Decreased |
| Overall Well-being | Improved | Deteriorated |
By prioritizing health education, we empower women not only to navigate their unique health conditions but also to inspire future generations to prioritize their health. Together, we can create a healthier, more informed society where women’s unique health needs are addressed with compassion and understanding.
Frequently Asked Questions
What factors contribute to the differences in health conditions experienced by women and men?
Women and men experience health conditions differently due to a variety of biological, hormonal, and social factors. Hormones like estrogen and progesterone can impact how women respond to diseases, while differences in body composition and immune system functionality may also play a role. Additionally, social factors such as lifestyle choices, access to healthcare, and cultural attitudes toward health can create disparities in the way men and women experience and report their health issues.
Please click here to buy immune system booster for women supplements from Amazon.
How do hormonal differences affect women’s health compared to men’s?
Hormonal differences, particularly the influence of estrogen and progesterone, can greatly affect women’s health. These hormones can influence everything from mood and metabolism to the risk of developing certain diseases such as osteoporosis and heart conditions. For instance, women typically experience unique health changes during menstrual cycles, pregnancy, and menopause, leading to a varied health experience compared to men, who do not undergo these hormonal fluctuations.
Are there specific health conditions that predominantly affect women?
Yes, certain health conditions disproportionately affect women. These include autoimmune diseases, such as lupus and multiple sclerosis, which are more common in women. Additionally, conditions related to reproductive health, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and endometriosis, specifically impact women. Understanding these conditions is crucial, as they often require targeted treatments and awareness to ensure women receive appropriate care.
How can lifestyle choices influence the way women experience health conditions?
Lifestyle choices, such as diet, exercise, and stress management, can significantly influence women’s health. Women often face unique challenges, like balancing work and family life, which can lead to stress and affect physical health. Engaging in regular exercise, maintaining a balanced diet, and prioritizing mental health can help mitigate some health issues that women face, allowing for better overall health and well-being.
What role does research play in understanding gender differences in health?
Research is vital for uncovering the differences in how health conditions affect women and men. It helps identify specific symptoms, risk factors, and effective treatments tailored for each gender. Increased funding and focus on gender-specific health studies enable healthcare professionals to provide better, more informed care. As awareness grows, we can expect advancements in treatment approaches that cater to the unique health needs of women.